Graphic design, a blend of creativity and technology, has become a sought-after career. As the visual face of businesses and media, it's all about conveying messages through imagery and layout.
What Do You Learn in a Graphic Design Course? When you enroll in a Graphic Design Course in Ahmedabad or any other tech hub that provides high-quality courses, you will get foundational knowledge and practical application. Key areas of focus include:
- Fundamentals: The mastery of colour theory, typography, and layout design.
- Tools: Proficiency in Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign.
- Practical Skills: Engaging with real-world projects such as logos, websites, and print materials.
What is the best way to learn Graphic Design? Determining the suitable learning path requires consideration of individual preferences and objectives. Here are some recommendations:
- Self-Study: Exploration of online platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and YouTube.
- Formal Education: Enrollment in universities or design schools for structured learning.
- Practice: Commitment to personal projects or freelancing to refine skills.
For those embarking on the journey as a beginner, courses are readily available to suit various needs. But if you want to learn it on your own, then this is the right blog for you!
Here we will discuss the step-by-step process of learning Graphic Design:
- How To Learn Graphic Design?
- Learning the Basics
- Design Programs
- Online Courses and Resources
- Creating a Portfolio
- Networking and Work Experience
- Continuing Education
Best Way To Learn Graphic Design
Wondering what is the best way to learn Graphic Design? Here's a step-by-step guide for mastering Graphic Design in six months based on the provided details.
Month 1: Understanding Basic Principles
- Balance and Alignment: Learn how symmetry and asymmetry play into design. Practice grid layouts.
- Contrast and Repetition: Experiment with visual dynamics and consistency.
- Proximity and Space: Focus on relationships between elements, grouping, and spacing.
- Colour Theory: Start with colour psychology and harmony.
Month 2: Typography and Layout Design
- Font Selection: Explore different fonts and their tones.
- Line Height and Spacing: Adjust spacing for readability.
- Grid Systems: Utilize grids for visual organization.
- Visual Hierarchy: Practice guiding the viewer's eye through design.
Learn how you can become a Graphic Designer, no matter at what stage of your career you are at : How to Become a Graphic Designer at Any Stage of Your Career?
Month 3: Imaging and Illustration
- Image Selection and Manipulation: Utilize tools like Photoshop for editing.
- Creating Custom Illustrations: Learn to create illustrations in Adobe Illustrator.
Month 4: Software Tools Mastery
- Adobe Creative Suite: Become proficient in Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign.
- Other Tools: Explore Sketch, Figma, CorelDRAW, and other specialized tools.
Month 5: Practical Application
- Real-World Projects: Apply your skills through client or personal projects.
- Portfolio Development: Begin building your portfolio, selecting your best works.
Month 6: Online Resources and Design Programs
- Online Resources: Utilize platforms like Adobe Tutorials, Google Fonts, Dribbble, Behance, etc.
- Design Programs: Master popular design programs such as CorelDRAW, Sketch, Figma, Blender, etc.
However, if this self-guided path seems overwhelming, one might consider enrolling in a Graphic Design Course with placement. Such a course could offer a structured curriculum, mentorship from experienced designers, and perhaps even placement opportunities, ensuring that your learning is comprehensive and aligned with industry demands.
Learning the Basics

Let’s understand the basic principles of graphic design and how to apply them:
Balance and Alignment
Balance provides stability and structure to a design. Whether it's a symmetrical or asymmetrical layout, alignment ensures elements have a pleasing connection, creating an orderly appearance. Utilizing grids can aid in achieving this balance.
Contrast and Repetition
Contrast adds visual intrigue, guiding the viewer's attention to key areas. Utilizing bold vs. subtle, and large vs. small, creates dynamics in the design. Repetition, meanwhile, unifies the design by reiterating specific styles or elements, providing visual consistency.
Proximity and Space
Elements close together are perceived as related, while spacing provides breathing room. Proximity helps in grouping related items, making the design user-friendly, while appropriate spacing enhances readability and overall aesthetics.
Colour Theory
Understanding Color Psychology
Colours have the power to influence emotions and perceptions. Red may signify urgency; blue can induce calm. Understanding these associations is vital in conveying the right message through design.
Color Harmony
Achieving harmony between colours adds visual appeal. Utilizing complementary or analogous colours can create a cohesive look. Tools like the colour wheel assist in forming balanced colour combinations.
Typography
Font Selection
Fonts communicate the design's tone. Serif fonts may signify tradition; sans-serif may look modern. Matching the right font with your design's message ensures coherent visual communication.
Line Height and Spacing
Proper spacing and line height contribute to legibility. Too cramped, and it's hard to read; too spaced out, and it loses coherence. Fine-tuning these elements enhances readability.
Layout Design
Grid Systems
Grids facilitate alignment and consistency, providing a skeleton for your design. They guide the placement of elements, helping to achieve a visually organized layout.
Visual Hierarchy
Creating a hierarchy helps guide the viewer's eye. By using size, colour, and spatial relationships, you can lead the viewer through the content in a logical, engaging manner.
Imaging and Illustration
Image Selection and Manipulation
High-quality images reinforce your message. Knowing how to use tools like Photoshop to edit and enhance images is fundamental. Custom adjustments can tailor images to your specific needs.
Creating Custom Illustrations
Unique illustrations add a personal touch. With tools like Adobe Illustrator, designers can craft custom illustrations that align with the brand and message, giving your design an exclusive feel.
Software Tools
Adobe Creative Suite
Proficiency in Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign is almost mandatory in today's design world. These tools offer extensive capabilities in photo editing, illustration, and page layout.
Other Tools
Various other tools cater to specific needs. Sketch and Figma excel in UI/UX design, while CorelDRAW is renowned for vector graphics. Familiarizing yourself with these broadens your design capabilities.
Practical Application
Real-World Projects
Engaging in real-world projects solidifies your understanding. Designing for actual clients or personal projects allows you to apply what you've learned, refining your skills.
Portfolio Development
Your portfolio is a visual resume. Carefully selected works showcase your ability and style, offering potential employers or clients insight into what you can achieve.
Best Resources To Learn Graphic Design

Here are some of the best resources for Graphic Design that will help you build your skills:
- Adobe Tutorials: Adobe offers tutorials for Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign. These resources are suitable for all skill levels.
- Google Fonts: Google Fonts is an open-source collection of fonts. It helps in understanding typography and font usage.
- Dribbble - Inspiration and Networking: Dribbble offers inspiration, trends, and professional networking opportunities.
- Behance - Portfolio Building: Behance is an online platform for portfolio building and networking with other designers.
- GIMP - Free Image Editor: GIMP is a free image editor with tutorials on photo retouching and image composition.
- World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) - Web Standards: W3C sets the guidelines and standards for web accessibility.
- SVG Edit - Scalable Vector Graphics: SVG Edit is a tool for creating and editing Scalable Vector Graphics.
- Unsplash - High-Quality Images: Unsplash provides free, high-quality images that can enhance any design project.
- Awwwards - Website Inspiration: Awwwards recognizes excellence in web design, offering inspiration from top designers and agencies worldwide.
- GitHub - Collaboration and Version Control: GitHub is essential for designers working in collaborative environments. It helps in version control and team collaboration.
- Blender - 3D Graphics: Blender is a free, open-source tool for creating 3D graphics. Tutorials and community forums are available to guide beginners.
- InVision - Prototyping: InVision provides tools for prototyping, collaboration, and workflow integration. It's highly valuable for user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) designers.
- Colour Hunt - Color Palettes: Color Hunt offers curated color palettes. It's an excellent resource for finding harmonious color combinations for design projects.
- Font Squirrel - Free Fonts: Font Squirrel is another reputable source for free, high-quality fonts, all hand-selected to ensure top-notch quality.
- SketchUp - 3D Modeling: SketchUp offers 3D modeling capabilities for everything from simple designs to complex architectural projects.
These tools and platforms provide comprehensive support in various facets of graphic design.
Design Programs: Mastering the ins and outs of popular design programs

The graphic design industry relies heavily on specialized software to create, edit, and finalize designs.
Here's a look at some of the most popular design programs, along with insights into their unique features and applications.
- Adobe Photoshop: Adobe Photoshop is the industry standard for photo editing and manipulation. From retouching to layering complex compositions, its extensive range of tools caters to both beginners and professionals.
- Adobe Illustrator: Adobe Illustrator is synonymous with vector design. It's used for creating logos, icons, and illustrations that can be scaled without losing quality.
- Adobe InDesign: Adobe InDesign specializes in layout design, perfect for magazines, brochures, and other print media. Its grid system allows for precise alignment and formatting.
- CorelDRAW: CorelDRAW offers similar capabilities to Illustrator but adds unique features like built-in 3D effects and a customizable user interface.
- Sketch: Sketch is primarily used for UI/UX design. With its plugin ecosystem and collaborative features, it streamlines the design workflow, especially in team environments.
- Figma: Figma allows real-time collaboration, making it popular for UI/UX design. Its cloud-based nature ensures that team members can work together seamlessly, even from remote locations.
- Blender: Blender is an open-source program for 3D modelling, animation, and rendering. It's an all-in-one solution for creating complex 3D designs.
- Affinity Designer: Affinity Designer is an alternative to Illustrator with powerful vector design capabilities. It provides a flexible and cost-effective solution for freelancers and small businesses.
- GIMP: GIMP is a free alternative to Photoshop, offering robust image editing features without the hefty price tag.
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is the go-to software for architects and engineers. It facilitates 2D and 3D design and drafting.
- Canva: Canva simplifies graphic design with drag-and-drop features. Though not as robust as Photoshop or Illustrator, it's user-friendly for non-professionals.
- QuarkXPress: QuarkXPress is another layout design tool, similar to InDesign, but with distinct features like responsive HTML5 content creation.
- InVision Studio: InVision Studio focuses on prototyping and interactive design, bridging the gap between static designs and final products.
- Cinema 4D: Cinema 4D is used for 3D modelling and animation, offering a broad array of features for motion graphics.
- Lightroom: Adobe Lightroom is essential for photographers, providing comprehensive tools for editing and organizing large volumes of photos.
- Paint.NET: Paint.NET is a free alternative to traditional painting tools, suitable for simple tasks and hobbyists.
Mastering these design programs is integral to a successful career in graphic design. However, understanding how to use them in a real-world context requires guidance and mentorship.
Enrolling in a graphic design course with placement not only provides comprehensive training in these tools but also ensures a smooth transition into the professional realm.
Creating a Portfolio: Building a portfolio of projects to showcase your work
Building a portfolio is like crafting your visual resume. It's more than just a collection of your work; it's a reflection of your style, skills, and creativity.

Whether you're a novice or a seasoned professional, these aspects can guide you in making an impactful and memorable portfolio.
Know the step-by-step process to become a Graphic Designer after 12th: How To Become a Graphic Designer After 12th?
Conclusion
Enrolling in courses offers an optimized pathway to learn Graphic Design from scratch. Guided by professionals, students not only master the essentials but also align their skills with industry demands.
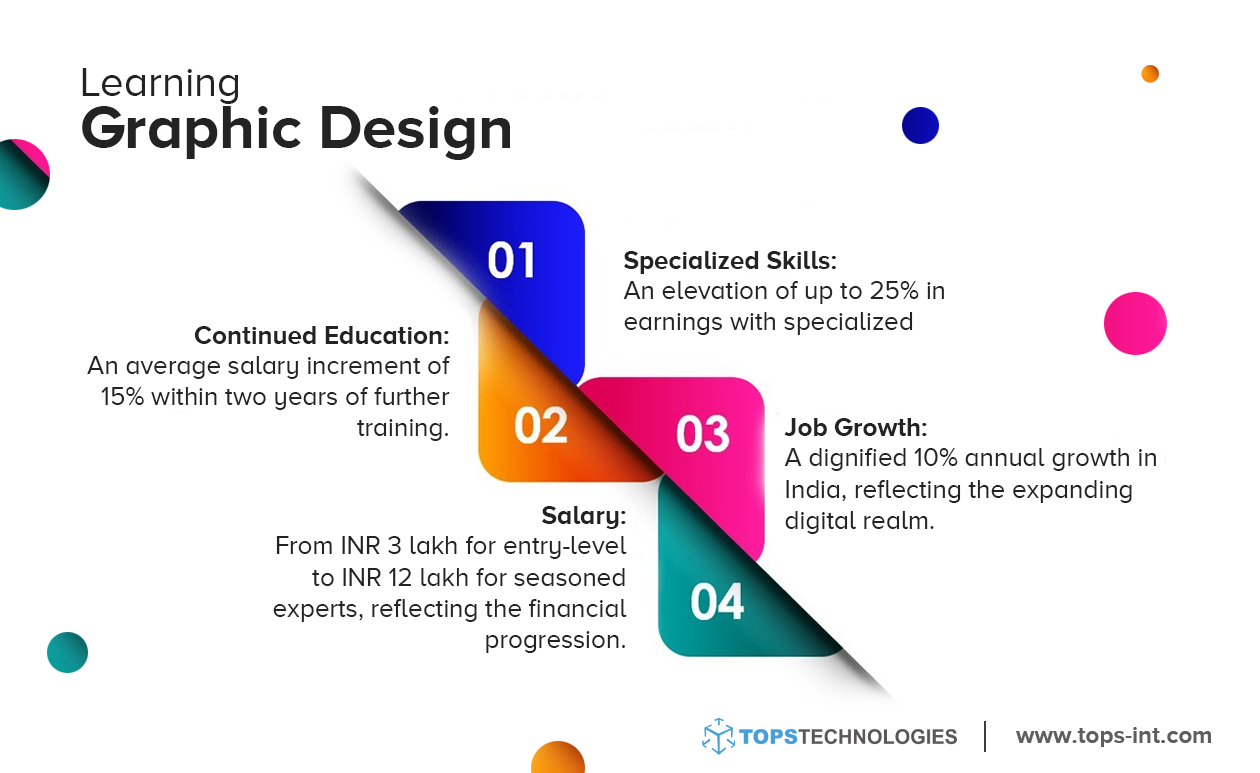
Statistics show that those who undertake structured courses are likely to earn 25% more compared to self-learners.
TOPS Technologies, a leading name in the field, has showcased this with their remarkable achievements: placing 1 Lac+ student, having tie-ups with 3000+ companies, and establishing 19+ offices across India. Whether you are looking for a Graphic Design course in Vadodara or any other city, reach out to TOPS Technologies!
If you're considering a career in graphic design, a diploma from a reputable institute like TOPS Technologies could be your pathway to success.
FAQs
How can I start learning graphic design?
You can begin with online tutorials and books or enroll in structured courses such as a graphic design diploma course for a well-rounded education.
What skills should a graphic designer have?
Fundamental skills include understanding layout, typography, colour theory, and mastering design software. Practical experience and a strong portfolio enhance employability.
How long does it take to complete a graphic design diploma course?
A graphic design diploma course typically ranges from 6 months to 2 years, offering both foundational knowledge and specialized skills in graphic design.
Is a graphic design course with placement a good option for career growth?
Yes, a graphic design course with placement ensures you receive professional guidance, real-world experience, and a smooth transition into the industry, enhancing career prospects.
Can I learn graphic design if I don't have any artistic skills?
Certainly! graphic design blends creativity with technical skills. While artistic flair can be beneficial, many courses teach you the necessary design principles from scratch.










