Venturing into the world of technology, we encounter buzzwords such as "Artificial Intelligence," "Machine Learning," and "Deep Learning." But what is the fine line when Artificial Intelligence Comparison is done with Deep Learning and Machine Learning.
These terms are often used interchangeably but have different scopes and applications:
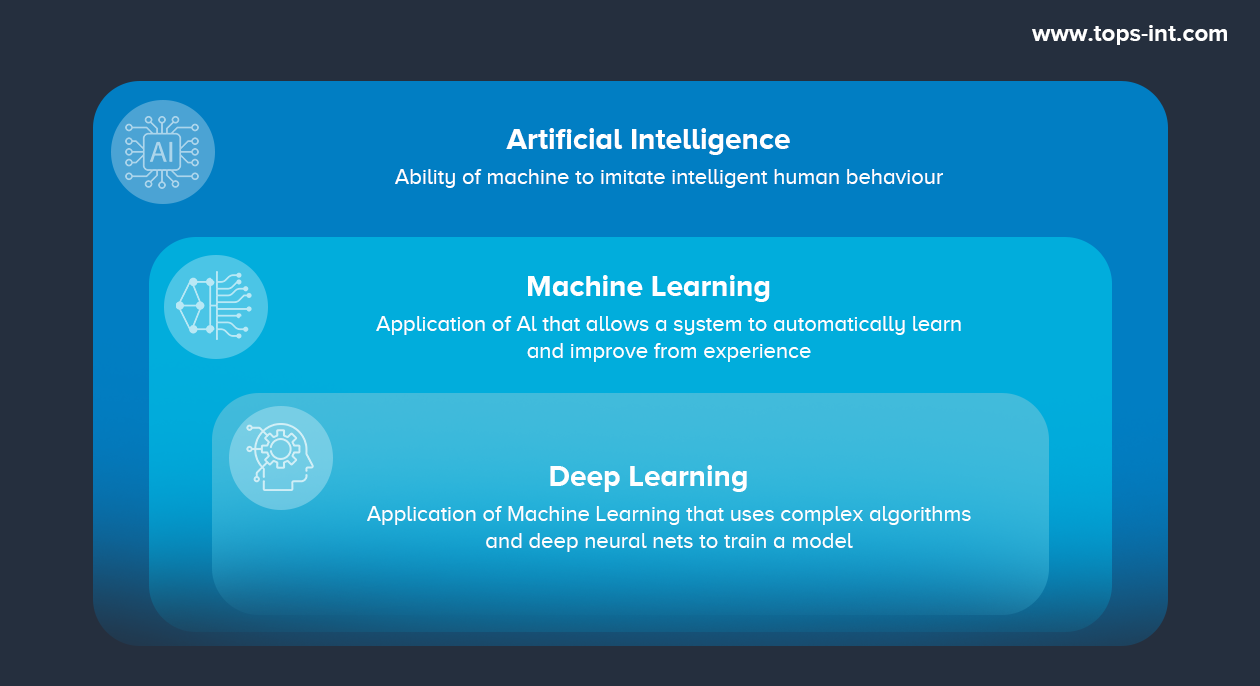
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): This is the granddaddy of the trio. AI refers to machines performing tasks in a way that mirrors human intelligence. It's the umbrella term under which ML and DL fall. For anyone who wants to start a career in this field doing an Artificial Intelligence Course is a must!
- Machine Learning (ML): This is a subset of AI. ML involves training machines to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning (DL): This is a specialized ML subset. It's all about neural networks with several layers - hence the term "deep." These layers enable machines to mimic the human brain, learning from large amounts of data.
Together, these three concepts form the backbone of intelligent systems. Let's untangle these terms and delve deeper to understand their roles and interrelationships better.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), as the name implies, imitates human intelligence processes by machines, primarily computer systems. It's an extensive field of study in computer science that equips machines to mimic human behaviour. The core idea? Enable machines to react and respond to situations just like humans would. Now, let's break down this overarching concept.
Understanding Human-like Behavior
AI aims to equip machines with capabilities such as:
- Learning: Absorbing new information and rules, then applying them to future tasks.
- Reasoning: Using rules to reach definite or approximate conclusions.
- Problem-solving: Identifying patterns and making logical deductions.
- Perception: Interpreting sensory inputs to understand the surrounding environment.
- Language understanding: Comprehending and communicating in a human language.
If successfully implanted, the above capabilities help machines function seamlessly in complex, real-world environments.
Two Distinct Branches of AI
AI is broadly classified into two categories:
- Narrow (or Weak) AI: These AI systems excel at specific tasks. For example, personal digital assistants like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant or recommendation engines on e-commerce websites. Here, the AI is only as intelligent as the specific task it's designed for.
- General (or Strong) AI: This is the advanced branch of AI designed to understand, learn, adapt, and implement knowledge across a broad range of tasks, much like a human. We're still in the conceptual and research phase regarding General AI.
You can enroll in an Artificial Intelligence Course to get started in the field of AI and land a high-paying job!
Techniques in AI: Rule-based Systems and Learning Systems
There are primarily two techniques involved in AI:
- Rule-based systems: Here, the AI system follows predefined rules. These rules guide the system to make decisions and perform tasks. These systems are quite common in fields like finance and legal, where defined logic works well.
- Learning systems (ML and DL): Machine and Deep Learning systems learn from the data rather than following a rigid set of rules. They improve their performance as they process more data. To learn more about these techniques in-depth you should enroll in a Machine Learning Course.
Here are the three diagrams illustrating the concepts of Rule-based Systems and Learning Systems in AI:
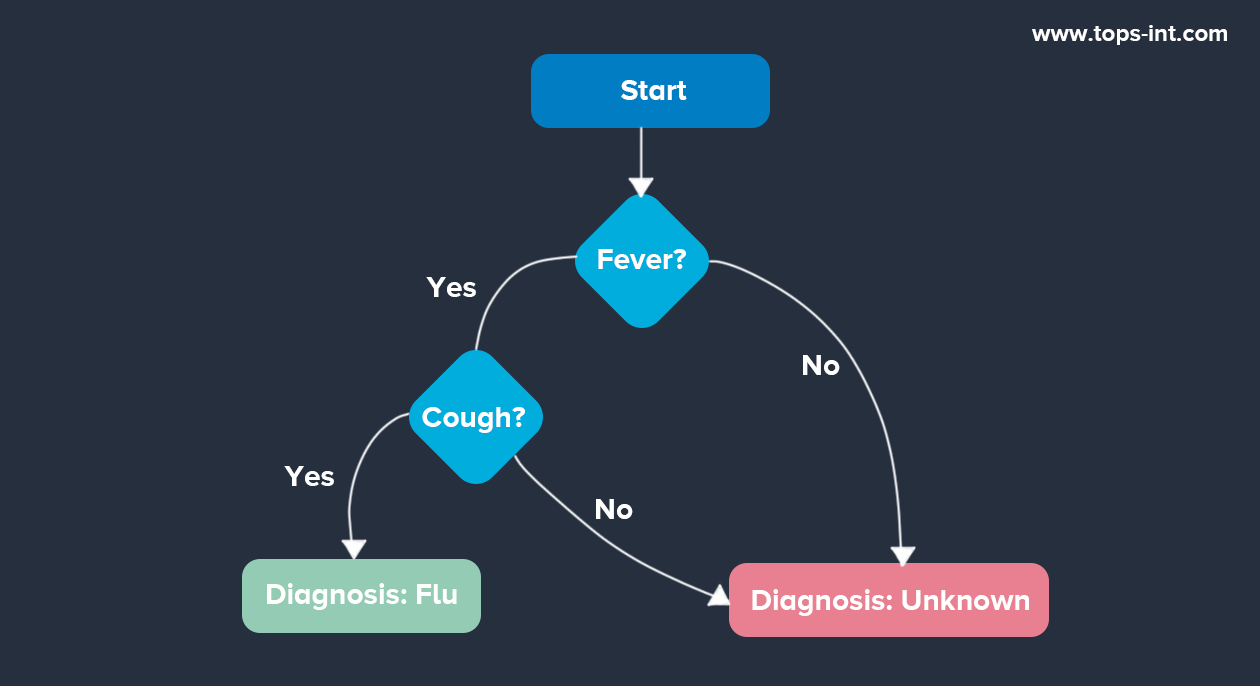
Diagram 1: Flowchart of a Rule-based System
This diagram represents a simple rule-based system for diagnosing the flu. The system starts by checking if the patient has a fever. If not, it diagnoses the condition as unknown. If the patient has a fever, it then checks for a cough. If the patient has both a fever and a cough, it diagnoses the flu. Otherwise, it again diagnoses the condition as unknown.
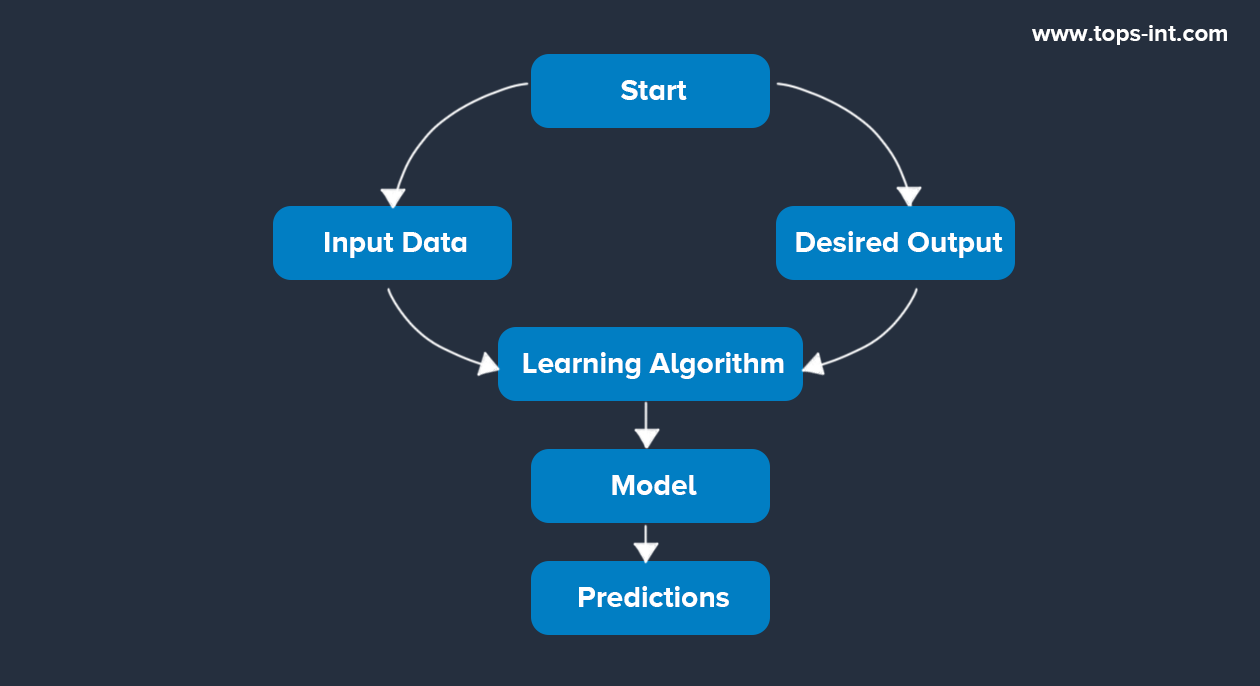
Diagram 2: Flowchart of a Learning System (Supervised Learning)
This diagram represents a supervised learning system. The system starts with input data and the corresponding desired output. These are fed into a learning algorithm, which generates a model. This model can then be used to make predictions.
Diagram 3: Comparison of Rule-based and Learning Systems
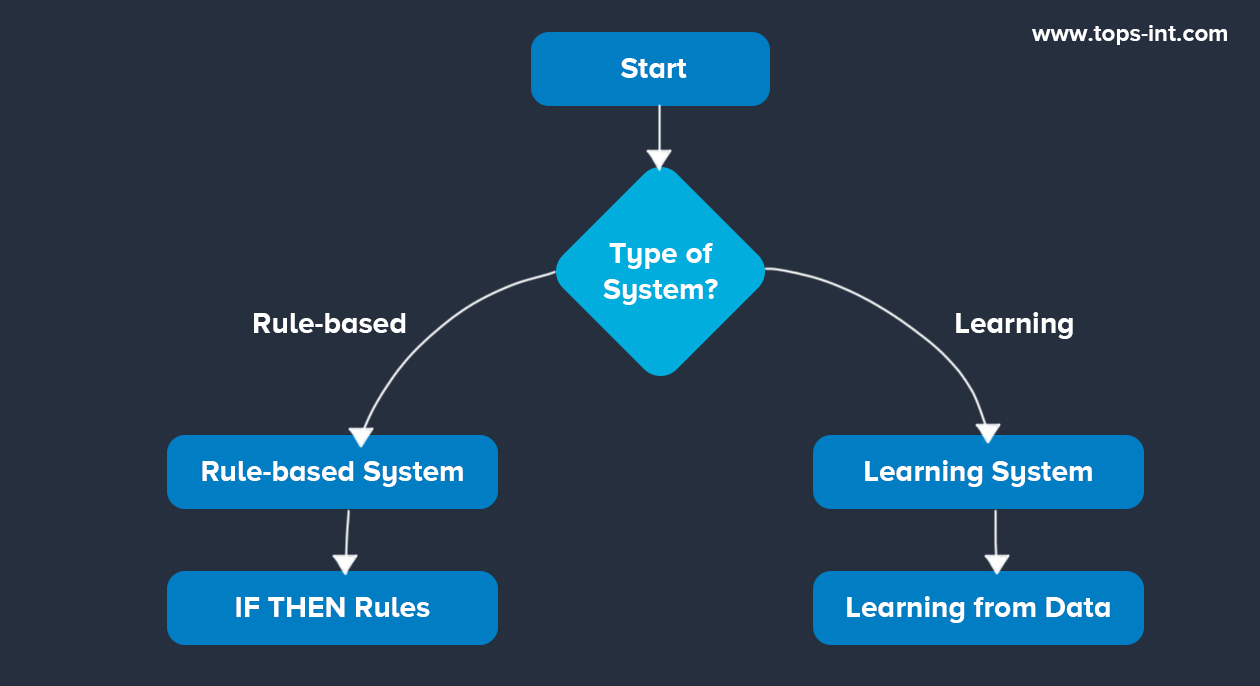
This diagram compares rule-based and learning systems. A rule-based system uses predefined IF-THEN rules to make decisions, while a learning system learns from data to improve its performance over time.
Read More: Your Future as a Graphic Designer With AI
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a dynamic field of Artificial Intelligence that uses statistical techniques to give computers the ability to learn. Instead of explicitly programming the system, ML is about designing algorithms that allow a system to learn from data. Now, let's dissect this fascinating subject.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine Learning can be categorized into three types:
- Supervised Learning: Here, the system learns from labeled data. It's like learning under a supervisor. The system is trained with inputs (data) and their corresponding outputs (labels). An example would be a system learning to identify images of cats based on a dataset of images where each cat image is labeled 'cat.'
- Unsupervised Learning: This type doesn't rely on labeled data. The system tries to find structures and patterns in the input data on its own. A common use is in clustering, where similar data points are grouped together, like grouping customers for targeted marketing.
- Reinforcement Learning: Here, an agent learns how to behave in an environment by performing actions and seeing the results. The agent gets rewards for the right actions and penalties for the wrong ones, much like playing a video game. This method is used to train systems for tasks like autonomous driving.
To master the different types of Machine Learning more and more people are enrolling in Machine Learning Courses. There has been a significant rise in Machine Learning Courses In Ahmedabad.
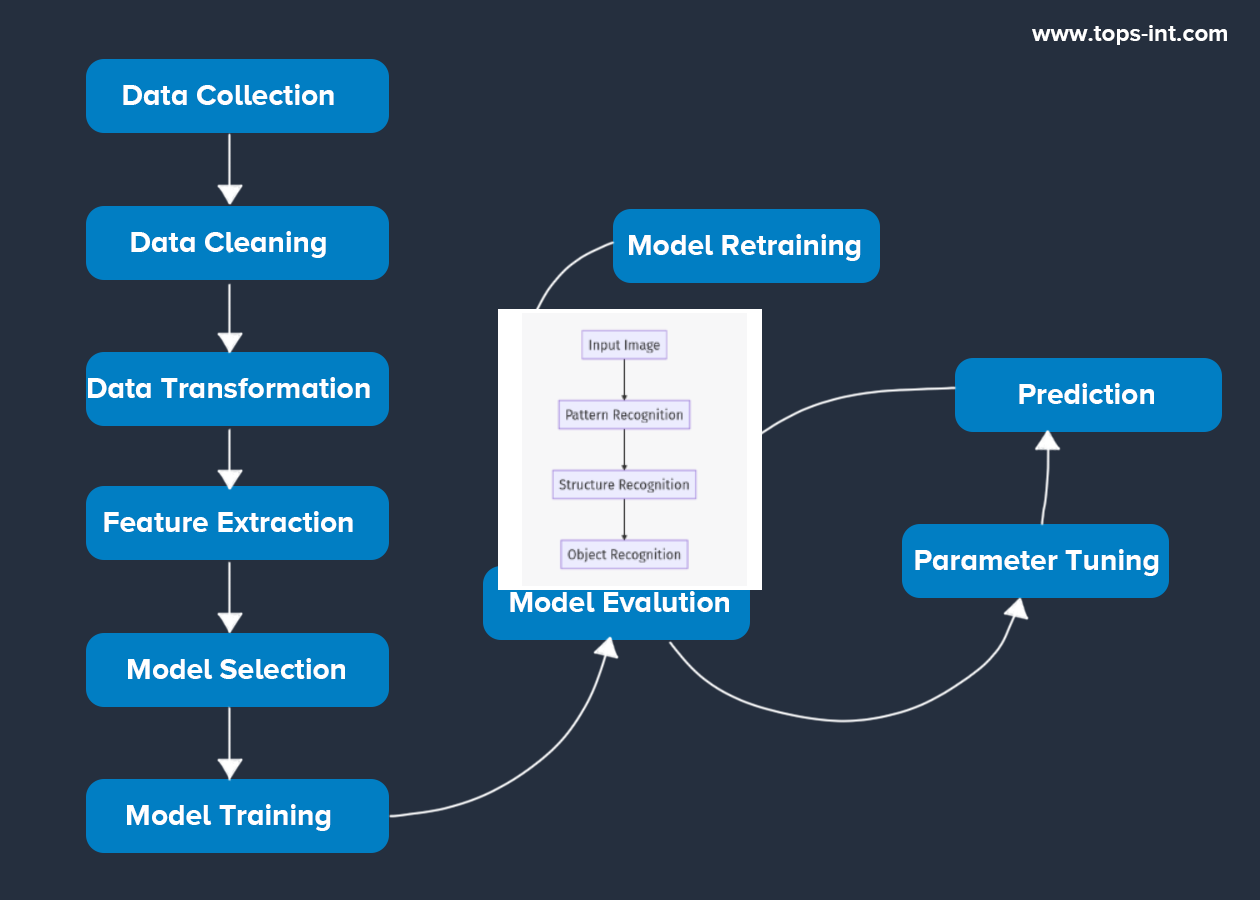
How Machine Learning Works?
- Data Collection: Collecting relevant data for the problem at hand.
- Data Cleaning: Removing noise and inconsistencies in the data.
- Data Transformation: Converting data into a format easily understood by the machine learning algorithm.
- Feature Extraction: Identifying the most relevant attributes or features in the data that will be useful for the machine learning model.
- Model Selection: Choosing the appropriate machine learning algorithm for the problem.
- Model Training: Training the model on the data involves feeding the data into the model and adjusting the model's parameters.
- Model Evaluation: Evaluate the model's performance using a separate set of data (the test set).
- Parameter Tuning: Adjusting the model's parameters to improve its performance.
- Model Retraining: If the model's performance is unsatisfactory, it is retrained with the adjusted parameters.
- Prediction: Using the trained model to predict new, unseen data.
Here is a more detailed diagram that represents the machine-learning process:
What is deep learning?
Deep Learning (DL), a subset of machine learning, is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain—specifically, it attempts to mimic the operations of a biological neuron in a format called artificial neural networks. DL leverages these networks to learn from large amounts of data. Let's dive deeper into this transformative technology.
Unveiling the 'Deep' in Deep Learning
The 'deep' in deep learning refers to the numerous layers in neural networks. These layers enable the system to break down tasks and process data at different abstraction levels, much like how our brain processes information.
Let's take an example similar to the one you provided:
Example 1: Recognizing Handwritten Digits
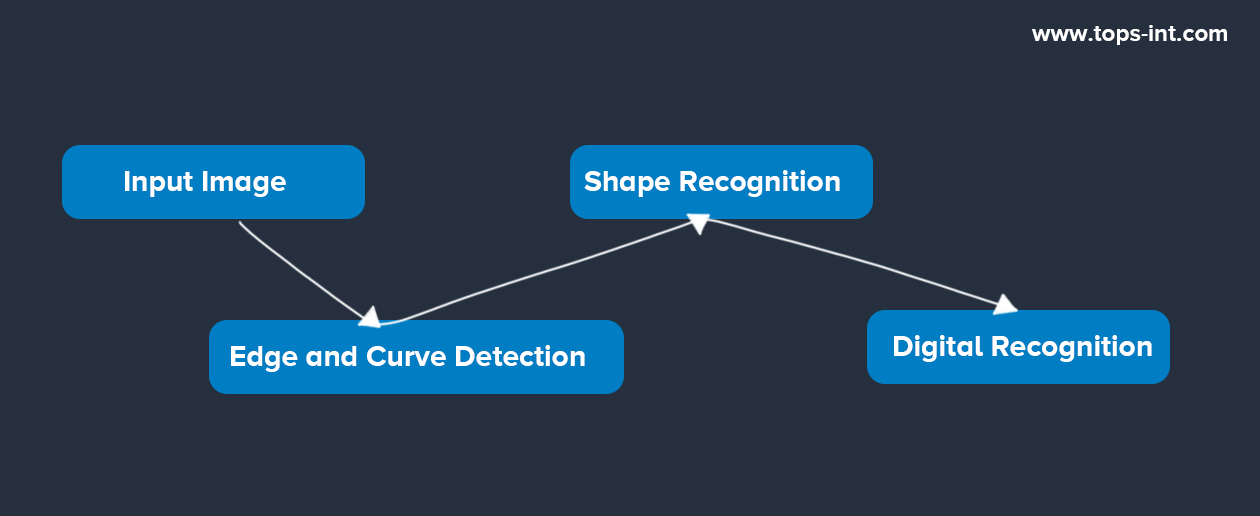
Think about how you'd recognize a handwritten number, say '2.' You'd likely check if there's a loop at the top, a diagonal or vertical line slanting down, and a horizontal line at the base.
A deep learning system does something similar but in a layered fashion:
- The first layer may just detect edges and curves in the image.
- The next layer combines these edges and curves to identify more complex shapes like loops or straight lines.
- Finally, the last layer combines these complex shapes to recognize the digit '2.'
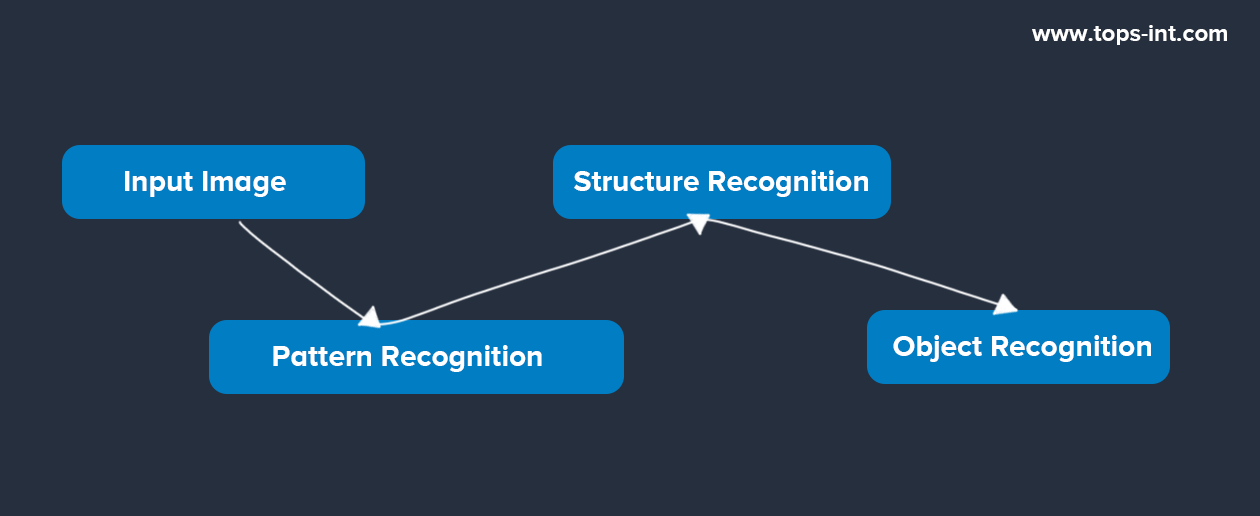
Example 2: Image Recognition – Cat vs. Dog
Now let's apply this to a more complex example. Suppose we need a system that can differentiate between images of cats and dogs.
In a traditional machine learning approach, we'd need to manually identify features like whiskers, ear shape, tail length, etc. But for a deep learning system, it's a different ball game.
The system is fed numerous images of cats and dogs, each labeled accordingly. It starts to understand features on its own:
- The initial layers might recognize simple patterns like edges and textures.
- Intermediate layers would combine these patterns to recognize complex structures like eyes, ears, or tails.
- The final layers would further combine these to recognize the whole object—either a cat or a dog.
This is an example of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), a type of deep learning architecture widely used in image recognition tasks.
Conclusion
The technological landscape is rapidly transforming with the rise of AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning.
TOPS Technologies, a premier IT training institute, is dedicated to equipping you with the right skills to navigate this change. Their expert-led, hands-on training in these revolutionary fields blends in-depth theoretical knowledge with practical, real-world applications.
Beyond gaining expertise, you'll receive career guidance and placement assistance, connecting you with top-notch companies looking for these skills. Even after your course ends, TOPS offers ongoing learning and support, keeping you updated in these fast-evolving fields. With TOPS Technologies, you don't just learn—you prepare for a promising future in the technology industry. Enroll today and take a step towards tomorrow's technology today.
FAQs
What is the difference between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
AI is a broad field focused on creating smart machines that mimic human intelligence. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, involves algorithms that allow machines to learn from data. There are many
Machine Learning Courses In Surat to help you learn Machine Learning! Deep Learning, a further subset of Machine Learning, uses artificial neural networks to mimic the human brain's functioning, allowing machines to learn from large amounts of data.
How does Machine Learning work?
Machine Learning works by designing algorithms that allow a system to learn from data. It recognizes patterns in the data and makes decisions or predictions based on these patterns. There are three types of Machine Learning: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning, each with different learning approaches.
Can you give an example of Deep Learning in everyday life?
One of the most common examples of Deep Learning is voice assistants like Apple's Siri or Amazon's Alexa. These devices use Deep Learning algorithms to understand and respond to human speech. Other examples include recommendation systems on Netflix or Amazon and facial recognition systems on social media platforms like Facebook.
What are the prerequisites for learning AI and Machine Learning?
A strong foundation in mathematics (especially statistics and algebra), basic programming skills (preferably in Python), and a good understanding of data structures are typically needed to start learning AI and Machine Learning. An introductory course in AI and Machine Learning, such as the ones offered by TOPS Technologies, can be a good starting point.
What job opportunities exist in AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
Job opportunities in these fields are vast and growing. Roles include Machine Learning Engineer, Data Scientist, AI Specialist, Research Scientist, and Business Intelligence Developer. Industries from healthcare to finance to entertainment seek professionals with AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning skills.